 |
The Marine Magnetics SeaSpy magnetometer was used. The towfish was kept 210 m off the stern, on the port side. The data was collected by the Marine Magnetics SeaLink software on the multibeam and transit lines,
The software integrated positional data by the NMEA GGA and ZDA strings delivered by two Trimble GPS receivers. From start to 2006-02-27T15:51:00 the ISMAR's receiver (POS2) was used, being directly connected to the magnetometer transceiver. After that timestamp the POS1 ship's GPS data were used, being run to the stern geophysical lab from the data distribution panel in the Acquisition room by using the ship's existing coaxial cable network. The whole sample will be repositioned on the POS1 data by checking magnetometer time with the 1 sec resolution positional data made available on one of the ship's server. The measured time offsets between GPS and Magnetometer clocks were applied. They were found to vary from -5/-6 sec when using the POS2 receiver (except the very first day of operation, when it was rougly 30 s), to -0.5/-1 sec when using the POS1 receiver.
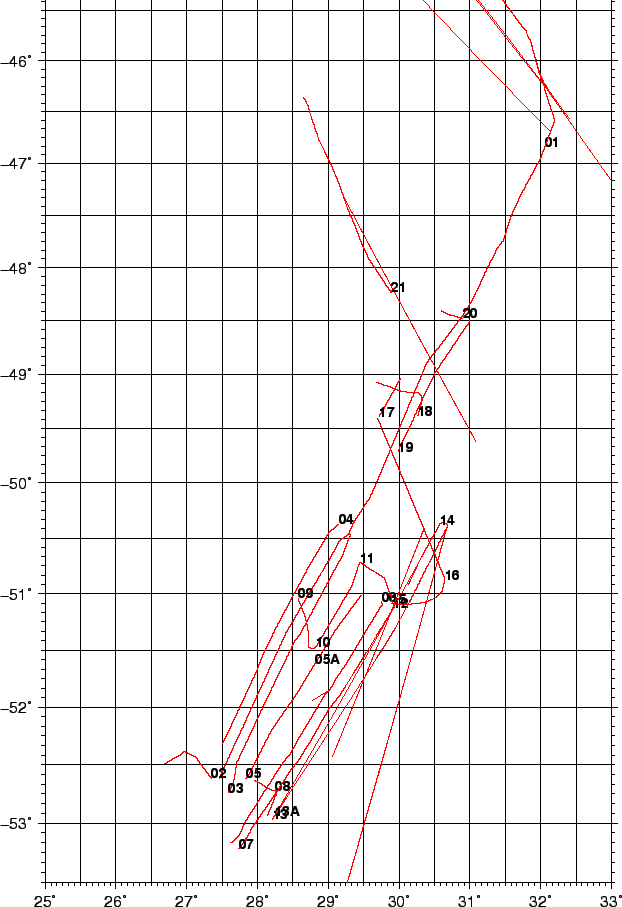
Figure 10 shows the acquired lines. Intersecting lines will be used to check and minimize day/night variations wherever possible.
The following data processing steps were applied:
The data of cruise KN145-L16 were provided as field data and were reprocessed with IGRF 2010 coefficients, thus achieving data consistency between the two datasets.
figure