 |
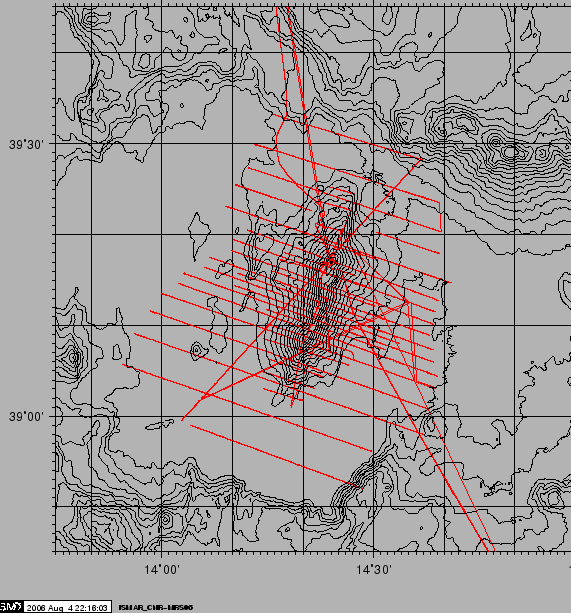
The ISMAR group used a Marine Magnetics SeaSpy magnetometer. The towfish was kept 120 m off the stern, on the port side.The data was collected by the Marine Magnetics SeaLink software on the multibeam and transit lines, The software integrated positional data by the NMEA GGA and VTG strings delivered by the ship's DGPS receiver. Figure 11 shows the acquired lines. Intersecting lines will be used to check and minimize trends, day/night variations, spikes and errors wherever possible.
figure
The following data processing steps were applied:
An example of the data can be viewed in Figures 13 and 12
The INVG team towed two Geometrics Mod-G811 magnetometers in a gradiometer configuration 150+150 m off the stern on the starboard side. The system console received the positional and time data from the ship's DGPS via NMEA GGA sentences. The data were QC checked and processed by the OASIS GEOSOFT software.
figure
figure